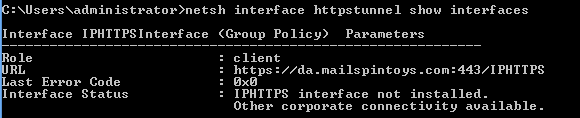
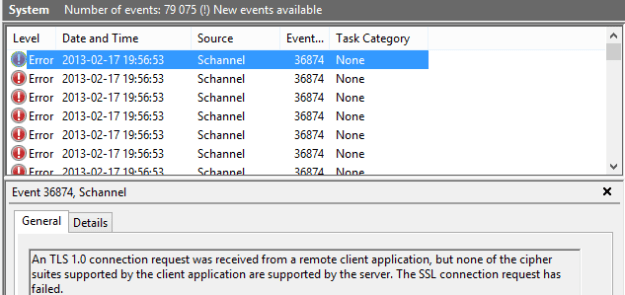
Most solutions today require certificates in some way, which means we need them even when setting up a lab/test environment.
If you for some reason don’t have a PKI/CA infrastructure in your lab environment you will most likely end up with a self signed certificates for web sites or other parts of your environment.
Since Windows 8/8.1 or Server 2012/2012 R2 there is a really nice PowerShell cmdlet that does that for us, without no hassle.
It can even handle multiple SAN’s.
It’s just to use the New-SelfSignedCertificate cmdlet from an elevated PowerShell window.
Example 1: Create and export one certificate with the name test.365lab.net:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName test.365lab.net -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My
#Export certificate to c:\test_365lab_net.pfx with the password 'Password'. (the thumbprint is found in the output from the New-SelfsignedCertificate command.)
Export-PfxCertificate -Cert cert:\LocalMachine\My\5D46460D29FE8E0C3F644D8ABA3C707AA83AFC79 -FilePath c:\test_365lab_net.pfx -Password (ConvertTo-SecureString -String "Password" -Force -AsPlainText)

Example 2: Create self signed SAN certificate with the names test.365lab.net,sts.365lab.net and 365lab.net:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName test.365lab.net,sts.365lab.net,365lab.net -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My

To check out your newly create certificates in the GUI, fire up the Computer Certificates Store mmc, which from Windows 8 / Server 2012 and above can be started with ‘certlm.msc‘ (OH YES!).

Note that I generally never recommend doing self signed certificates in production environments, they are only for testing purposes!
/Johan